On July 6, 2023, in collaboration with the research group of Fudan University's Professor Zi Jian, the research group of CQU's Han Dezhuan published a research paper entitled "General bound states in the continuum in momentum space” in Physical Review Letters, a top physics journal. Chongqing University is the first affiliation and the corresponding affiliation. Jiang Qiao, a young teacher of Chongqing University, and Hu Peng, a doctoral candidate (already graduated) of Chongqing University, are first co-authors of the paper. Han Dezhuan and Zi Jian are corresponding co-authors.
Photonic crystal slabs that support resonant modes have become an ideal platform for the study of polarization singular points in momentum space. In the momentum space, different types of polarization singular points, including vortex polarization singular points (Point V) and circular polarization states (Point C), have been revealed and observed in experiments. At Point V, there is no leakage in the corresponding Bloch mode as the far-field radiation disappears. Therefore, it is called the bound state in the continuous spectrum (BIC). While maintaining the symmetry of the photonic crystal slabs, by changing the system parameters, BIC can move continuously along the high-symmetry line in the momentum space. Latest studies have shown that BIC can be moved from high-symmetry line to non-high-symmetry point in momentum space by breaking all in-plane mirror symmetry of the system. However, whether BIC exists outside the high-symmetry line in momentum space without changing the symmetry of the photonic crystal slabs is yet to be figured out. In this Project, we studied the distribution and evolution of polarization singular points using polarization patterns in momentum space. Polarization singular points including Point V (BIC) and Point C correspond to the vertices of the polarization pattern. It can be proved that the topological charge of each plane in the polarization graph must be zero. This indicates that there is a non-local correlation between the polarization singular points at different Points k.
Based on the correlation between polarization singular points revealed in the above polarization graph, the group proved for the first time that BIC could exist in a stable manner outside the high-symmetry line of momentum space without reducing the symmetry of the system, and called this BIC "general BIC". Then, by changing the geometric parameters of the system, two interesting processes related to this general BIC were observed, including the consolidation of two general BICs and a BIC on a high-symmetry line, leading to the inversion of the topological charge of the latter, and the consolidation of two general BICs with opposite topological charges outside the high-symmetry line in the dynamic space, which eventually led to the annihilation of the topological charge.
This Project revealed the general existence of BIC in the momentum space of photonic crystal slab system, and provided a more comprehensive image of the distribution of BIC in the momentum space. The BIC outside the high symmetry line found by the team provided a new mechanism for the control of polarization singular point. It is of great significance for the study of controllable vector light field laser, vortex light field generation and light field polarization control. The research project has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation and the earmarked funds for colleges and universities allocated by the central government.
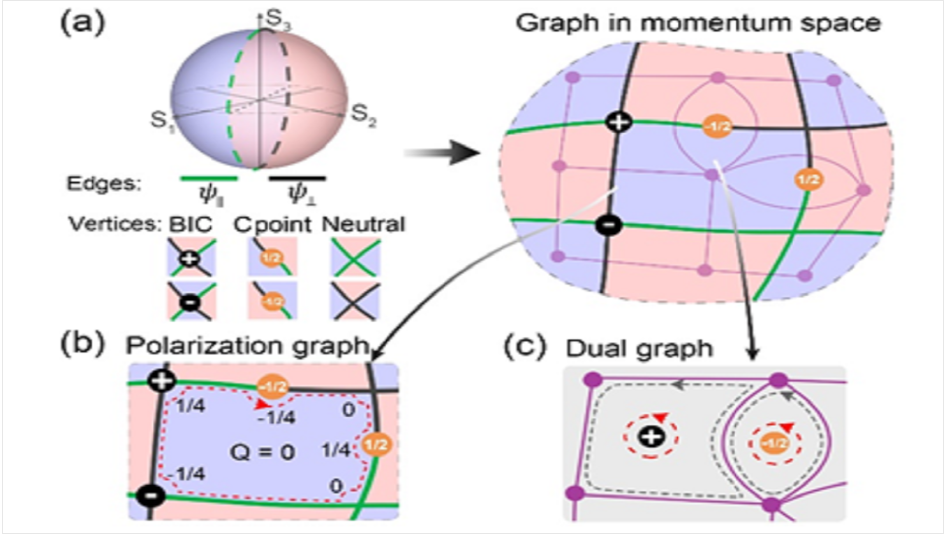
Figure: Polarization graph in the momentum space. (a) Polarization graph and its dual graph. BIC and Point C correspond respectively to the intersection and connection points of different color edges in the polarization graph. (b) The topological charge of the plane in the polarization graph is zero. (c) The topological charge of the plane in the dual graph is equal to that of the corresponding vertex in the polarization graph.
Link of the paper:
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.131.013801
